-
Solutions
Vendor Management Efficient vendor management platformField Service Management Effective onsite service operationsReal Estate Management Efficient real estate managementAsset Management Efficient asset lifecycle managementDealer Management System Analytics-based Smart Dealer ManagementDigital Retail Solution Integrated e-commerce solutionsSubscription and Billing System Automated billing and subscriptionsSales Force Automation Optimized sales process automationIntelligent Character Recognition Software Automated text conversion and data extraction
- Why Raapyd
- Insights
- About
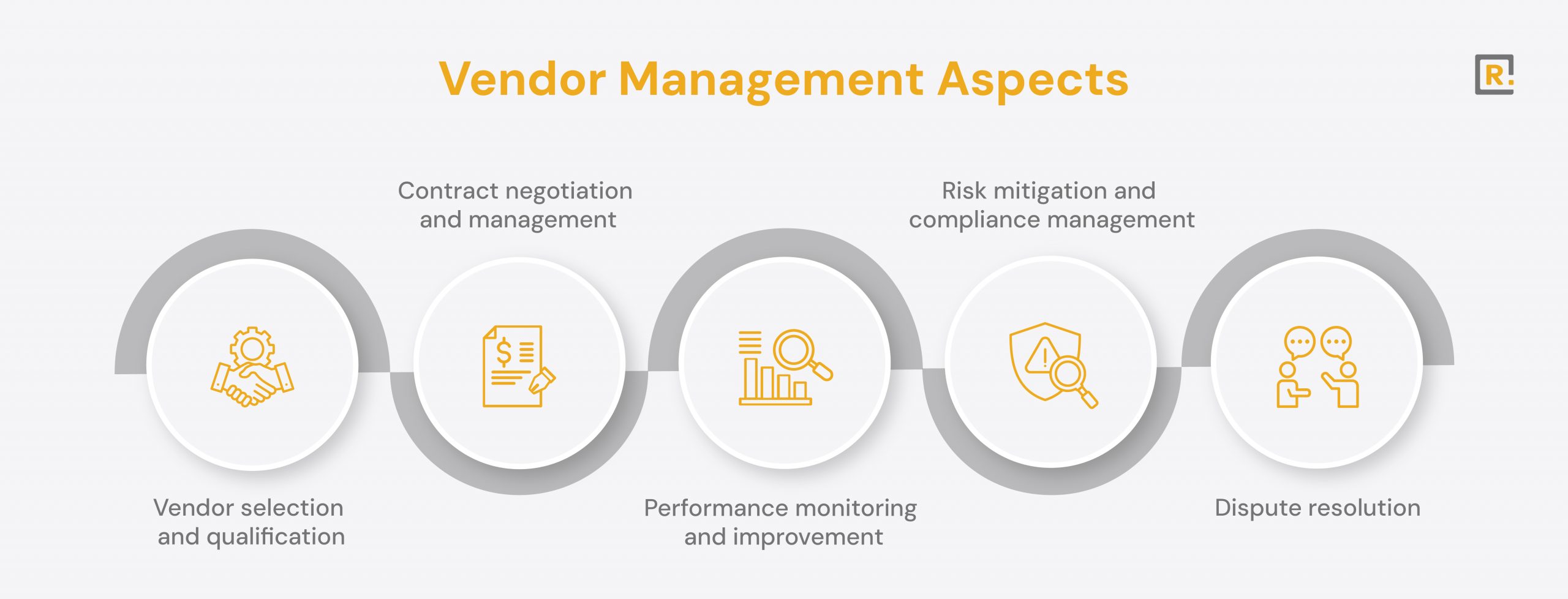
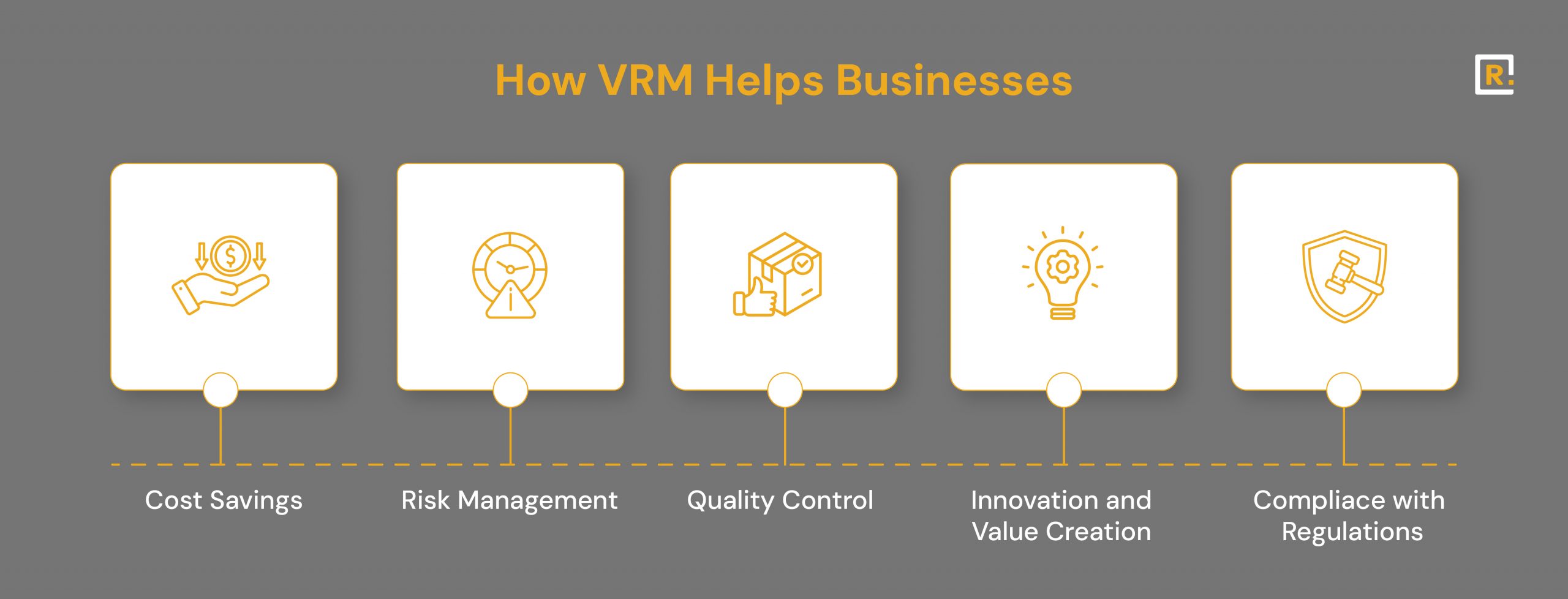
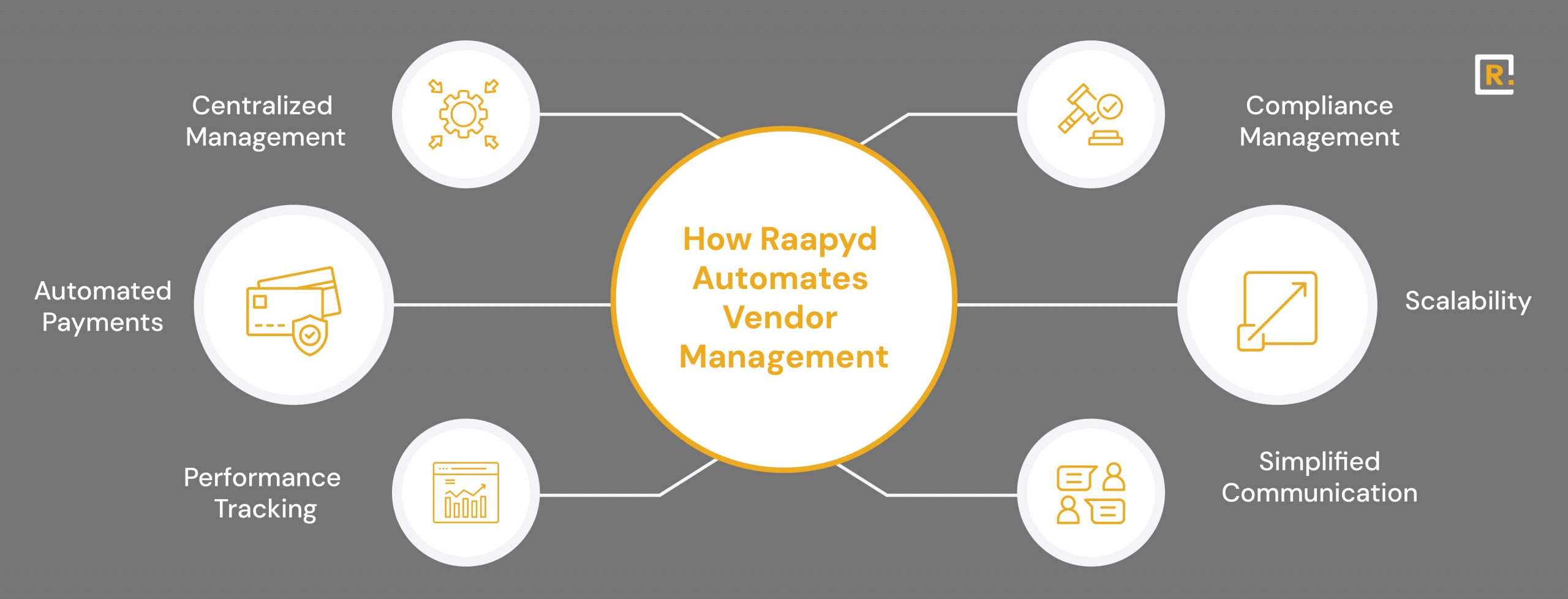
Vendor Relationship Management (VRM) is a strategic process that involves selecting, managing, evaluating, and optimizing the performance of external vendors that supply goods or services. VRM is important because it helps businesses reduce costs, improve product and service quality, mitigate operational and compliance risks, and build long-term partnerships that drive innovation and business growth.