-
Solutions
Vendor Management Efficient vendor management platformField Service Management Effective onsite service operationsReal Estate Management Efficient real estate managementAsset Management Efficient asset lifecycle managementDistribution Management System Optimized supply chain distributionDigital Retail Solution Integrated e-commerce solutionsSubscription and Billing System Automated billing and subscriptionsSales Force Automation Optimized sales process automationIntelligent Character Recognition Software Automated text conversion and data extraction
- Why Raapyd
- Insights
- About
Vendor Risk Management: Key Steps to Protect Your Business
- Vendor Management

Did you know?
Nearly 98% of organizations are affiliated with third-party vendors to execute their core operations.
Third-party vendors help businesses adopt a flexible approach, allowing them end-to-end access to various operations. For instance, these software programs help you access everything from software providers to logistics partners who will help businesses grow, innovate, and work efficiently.
However, any such increase in dependence on outside parties introduces new threats. Unless appropriately managed, the associated vendors can become the vulnerable link in the operational chain and expose firms to potential financial, operational, legal, or reputational damage.
What’s Changed in the Recent Years?
In recent years, vendor risk management (VRM) has emerged as a critical practice that modern organizations must take seriously to protect themselves from the dangers associated with such relationships.
This comprehensive guide will examine the different aspects of VRM and understand its importance, the risks involved, and best practices for successfully implementing a VRM program for business safety.
So continue reading as we learn more about VRM strategies that can shield your company from potential third-party pitfalls.
What is Vendor Risk Management?
Vendor Risk Management is a process for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring the risks associated with third-party vendors. Third-party vendors can be imperative in the form of a product or service administered daily, data processing, managing the supply chains, or as essential as the functioning of the core business. The higher the organizations’ dependence on vendors to enhance their ability to operate, the higher the risks associated with such partnerships.
At the core of VRM is ascertaining that vendors meet definite security, regulatory, and performance standards and mitigating the risks they may present. Financial instability of a vendor, non-compliance, or poor cybersecurity may prove a high stake in an organization’s operational effectiveness, creating vulnerabilities from legal compliance to data security. Vendor Risk Management allows organizations to do the following:
- Ensure vendor reliability and performance.
- Protection of sensitive data and information that is shared with the vendors.
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Minimize operation disruption in case of vendor failure.
As businesses increasingly digitized and many others outsource highly specialized services, VRM has become an essential routine practice in many organizations’ overall risk management. It provides a systematic approach to helping organizations shield their operations and reputation from vendor-related risks.
Types of Vendor Risk
Organizations face various levels of risk from different vendors based on their position in the business, nature of service, and access to sensitive information. In this regard, the following are the essential categories of risks that any organization must assess while dealing with third-party vendors.
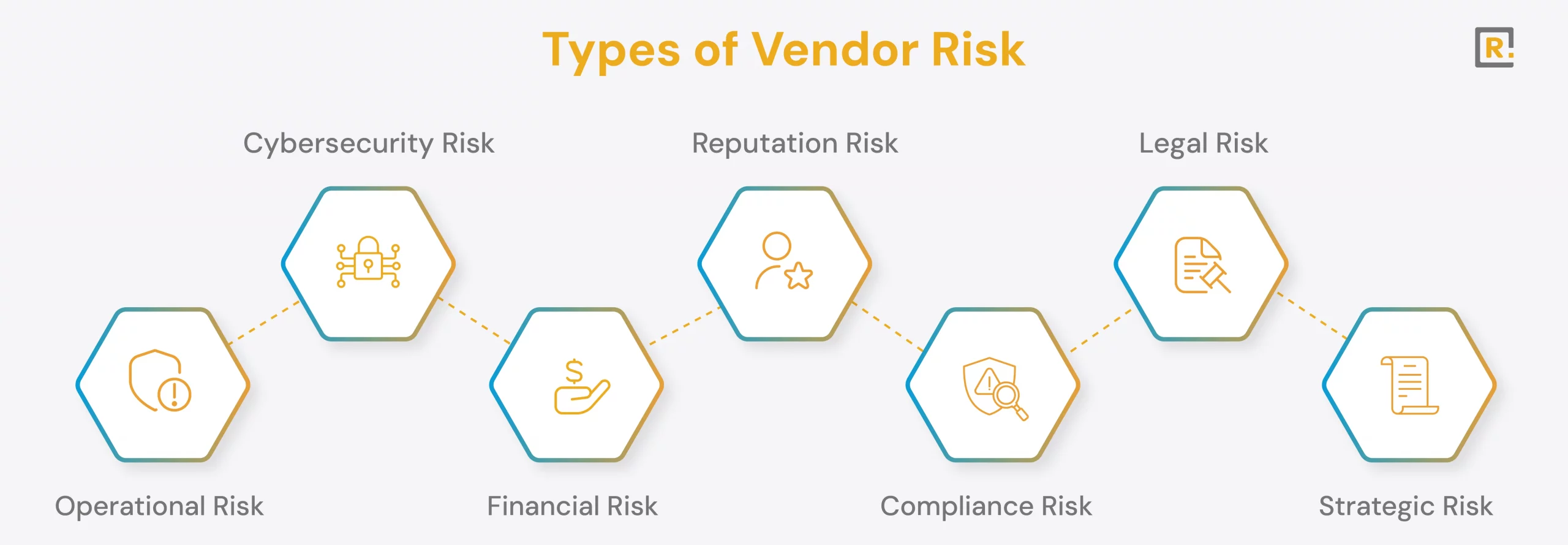
Operational Risk
Operational risk is the risk of a breakdown in your business process caused by your vendor. This may sometimes occur if many other reasons hamper the vendor’s performance- if the quality of service could be better, it has lost systems, or the product it promises to deliver needs to be delivered on time. For example, if a key IT infrastructure provider loses a minute, it costs your business to lose utilities or services.
Operational risk is influenced by factors like:
- The vendor cannot meet agreed contractual deliverables or binding service level agreements.
- Inadequate planning and disaster recovery of business.
- Inability to scale services to grow your business positively.
Cybersecurity Risk
As third-party vendors access your company’s data, networks, or systems from afar, the potential for cyber attacks grows. This means that, in case your partners have weak cybersecurity, they open your doors for attacks, data breaches, ransomware, or any cyber attack.
Indeed, in most high-profile data breaches, attackers gain access to the target company’s network via third-party vendors or their supply chains.
Key elements that lead to a risk in cybersecurity include:
- Poor security protocols from a vendor or no encryption.
- A lack of constant security audits and updating procedures.
- Vendor employees misuse sensitive information or systems.
Financial Risk
This happens when a vendor’s financial instability uniformly impacts the services or products they were contracted to provide. This can be most concerning when vendors form a critical link in your supply chain or business operations.
If a vendor files for bankruptcy or falls into financial trouble, this can disrupt your supply chain, slow down your operations, or even require you to replace them immediately.
Key factors contributing to financial risk:
- Vendor’s weakening financial condition or other insolvency signals
- Delays in the making of shipments hurt payments and deliveries
- Increasing expenses of substitute vendors
Reputation Risk
This is because vendors become an extension of your organization’s brand, meaning that their actions/behaviors reflect your company’s reputation. Although not directly, when a vendor is involved in unethical practices or legal offenses where, your business faces reputational damage through association. This may lead to a loss of customers and a reduction in trust, eventually translating to financial loss.
The factors that contribute significantly to this risk reputation are:
- Illegal or unethical activities by the vendor.
- Negative media concerning the vendor.
- The vendor is unable to maintain your product or service’s quality standards.
Compliance Risk
Compliance risks occur when vendors cannot uphold your organization’s legal and authorized regulations. This must be recognized, especially in industries that deal with sensitive information, such as health, finance, and specific government departments.
If non-compliance occurs, both types of fallout would involve the vendor and, secondly, your organization. These fallouts would include fines, litigation, and regulatory action.
Key factors contributing to compliance risk:
- Vendor’ not being compliant with industry-specific regulations (such as GDPR or HIPAA)
- Improper or absence of proper documentation or certification
- A Vendor’s security policy and practices could be better quality and more efficient.
Legal Risk
Contract breach and intellectual property breach disputes between an organization and the vendors it associates with can lead to expensive legal battles, fines, or penalties. These can occur when contracts must be appropriately designed and maintained.
Key factors contributing to legal risk:
- Poorly drafted contracts with ambiguously worded terms.
- Inadequate enforcement concerning confidentiality or non-compete provisions.
- Intellectual property infringement by the vendor.
Strategic Risk
This is when a vendor’s intentions or performance are in a way that hamper the ability of your organization to accomplish long-term business goals. For example, suppose a vendor cannot contribute innovations or increase the services your company requires as your company expands. In that case, your company might lose a crucial competitive position in the market.
Significant factors causing strategic risk are:
- Misalignment of vendor services with strategic objectives of your organization
- Lack of innovation by the vendor or his inability to keep pace with technological developments
- Over-reliance on a single vendor for critical services or products
Why is Vendor Risk Management Critical?
VRM plays a vital role in defending your organization from a wide range of threats emanating from third-party partnerships. Vendor failures have many risks; an organization may depend on vendors for IT infrastructure, cloud services, manufacturing, and logistics.
Here are a few reasons why a robust VRM program is of utmost importance:
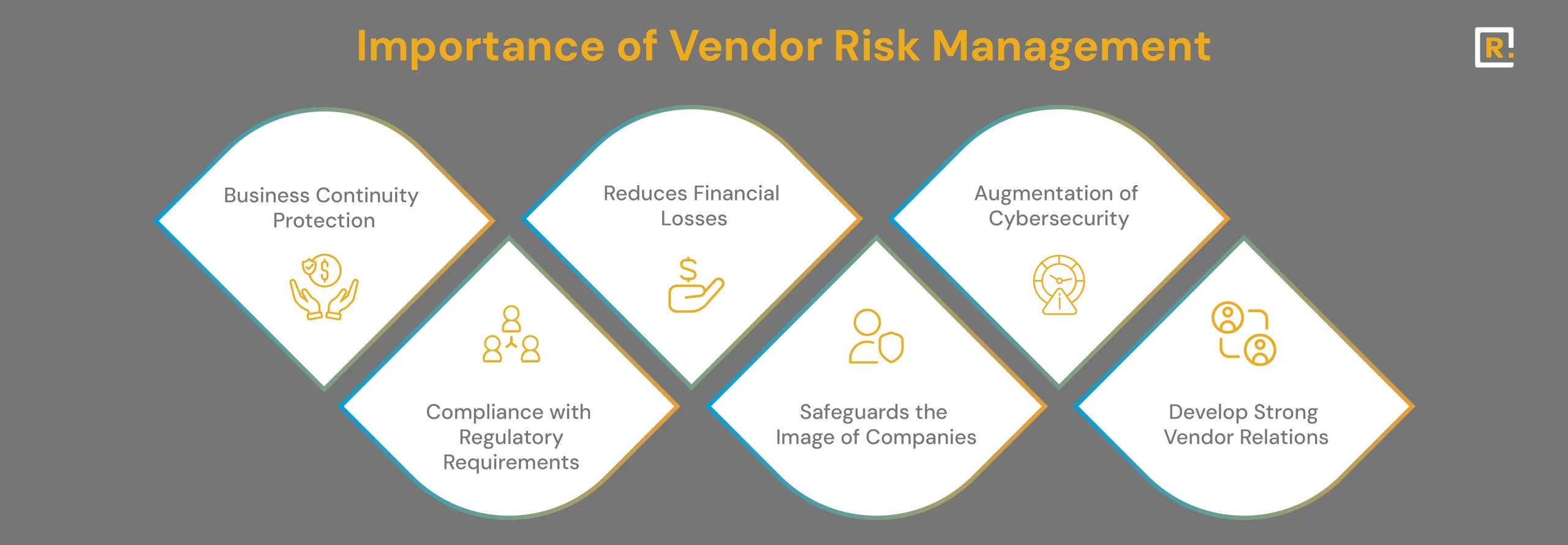
Business Continuity Protection
Failure of a vendor to deliver goods or services can ruin your firm. VRM ensures that your critical vendors are dependable and have plans strong enough to continue delivering service even despite adversity. Proactive risk management within the organization ensures sustained operational resilience even when the vendor is experiencing adversity.
Reduces Financial Losses
Vendor risks can lead to financial loss in several ways, including supply chain disruption, data breaches, regulatory fines, or legal litigation. VRM mitigates vendor risk by helping assess and mitigate risks.
In addition, these assessments will help negotiate contract terms and SLAs, which, in essence, lower financial exposures.
Augmentation of Cybersecurity
With the surging rates of cyberattacks, businesses must monitor the security measures enforced by their third-party vendors. Often, a vendor accesses corporate or customer-sensitive data or networks, which could potentially become a source of cybercrime.
Effective VRM guarantees that vendors can adhere to stringent cybersecurity requirements. It guarantees near-constant monitoring of their networks in compliance with the set standards, having the correct security protocols, and adhering to your business.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Many industries have stringent regulatory requirements regarding data security and privacy, among other things. Your organization can incur severe penalties if a breach occurs in one of your vendors.
VRM highlights the conformity of vendors with regulatory requirements to enable your company from risking a lack of compliance and result in reduced organizational legal and financial impact.
Safeguards the Image of Companies
What a vendor decides to do can affect your company’s reputation, mainly if they need to live up to ethical or legal standards. With the world being such a small place and bad news traveling fast, even one mishap by a vendor can hurt your brand. VRM safeguards your company’s reputation through pharmaceutical vetting and continuously monitoring your vendor’s performance.
Develop Strong Vendor Relations
A robust VRM program underpins healthy vendor relations in many ways: it allows you to set expectations and provide transparent, open communication while offering a channel for further communication.
This way, both parties find themselves easily aligned toward a goal, thus further reducing the chance of misunderstandings. The relationship built with the vendors will ensure better service delivery because they will feel more attached to their partner organizations.
Vendor Risk Management Best Practices
Organizations must adopt structured and systematic approaches to vendor risk management. Adopting the best VRM practices ensures that risks are identified early, mitigation measures are adopted, and vendor performance is tracked continuously.
Here are some of the top best vendor risk management best practices for effective VRM:

Formulate a Formal Vendor Risk Management Policy
An effective VRM policy can be the core element of a successful vendor risk management program. It should capture the processes for selecting vendors, risk assessment, ongoing monitoring, and contract management, as well as describe the roles and responsibilities within the organization for managing vendor risks.
Some critical components of a VRM policy include:
- Vendor selection and onboarding criteria
- Risk assessment and categorization process
- Continuous monitoring and audit procedures
- Incident response and vendor exit strategy.
Deep Due Diligence in Onboarding
It is essential to conduct due diligence before partnering with any vendor. This includes checking for financial stability, security, compliance, and performance record checks. Due diligence ensures that only a reliable vendor is associated with you and reduces the risk of associating with vendors that could threaten your organization.
The steps involved in due diligence are:
- Verification of the vendor’s financial health and creditworthiness
- Review of the history of litigation or regulatory enforcement actions taken against the vendor
- Evaluation of cybersecurity and data protection policies by the vendor
- Checking for appropriate certification or licensure by the vendor
Prioritize Vendors by Risk Rating
Vendors are not created equal. Some pose a greater risk to your institution than others. Categorize your vendors based on their level of risk so that your organization can focus its effort on risk management.
Vendors offering services essential to your survival or access to sensitive data will be most critical and require more stringent scrutiny and monitoring. Non-critical vendors require less frequent assessments.
Categorization of vendor risk may involve:
- High-Risk Vendors: Those vendors who provide vital services gain access to sensitive data or are involved in highly regulated industries.
- Medium-Risk Vendors: This group of vendors is crucial but needs to be mission-critical.
- Low-Risk Vendors: The vendors whose failure would have little consequence on your organization’s operations.
Continuously Monitor Vendor Performance
Vendor risk certainly does not end when a contract has been signed. Ongoing monitoring ensures vendors continue to act consistently with standard performance, remain compliant with changing regulatory requirements, and have sufficient security protocols.
Regular audits, performance reviews, and risk assessments enable the early identification of rising risks and allow organizations to implement corrective actions before escalation.
Monitoring your operations includes the following elements:
- Vendor conformance with SLAs and contractual obligations.
- Where applicable, consider the periodic evaluation of the vendor’s financial stability.
- Tracking information about security incidents and data breaches that involve the vendor.
- The assessment of the vendor’s reaction to regulatory changes.
Use sound contracts with transparent SLAs
Contracts are one of the most influential ways of managing vendor risk. A robust contractual agreement is well-positioned to clearly articulate both parties’ expectations, duties, and success metrics.
It should include penalties for non-observance, methods to resolve disputes and termination conditions. Built-in SLAs should also describe the level of service expected and the consequences of failing to meet those standards.
Some of the unique vendor contract components include:
- Clearly defined SLAs and performance metrics
- Confidentiality and data protection clauses
- Consequences of a breach of contract or a violation of the SLA
- Termination conditions and vendor exit strategy
Ensure Vendors Follow Cybersecurity Best Practices
Vendors accessing your networks, systems, or sensitive data should follow the best cybersecurity practices. These include encryption, multi-factor authentication, data backup procedures, and regular security audits.
Compliance of vendors with industry-specific security standards like ISO 27001 or SOC 2 also minimizes the potential for cyber risks.
Key measures for cybersecurity include:
- Regular vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
- Robust authentication mechanisms, like Multi-Factor Authentication
- Maintaining the encryption of sensitive data during transmission and storage.
- Backup of data and disaster recovery procedures
Develop a Vendor Exit Strategy
Not all vendor relationships last forever, and it may sometimes be necessary to exit the relationship due to performance, legal, or other risk issues.
An articulated vendor exit strategy aids in making a smooth transition from a vendor and minimizes disruption of business operations while ensuring sensitive data is securely returned or destroyed.
The following are the major components of a vendor exit strategy:
- Processes for a transition of services to another vendor
- Secure return or deletion requirements of organizational data
- Contract exit clauses: Conditions under which the contract could be terminated
- Contingency planning: To minimize operational disruptions.
Vendor Risk Management Challenges
It has challenges as vital as VRM is to protecting your business. Those challenges can be tough to overcome, whether implementing a robust VRM initiative or maintaining your existing VRM program in the face of growing complexity as you work with more and more third parties.
Here are some of the most common VRM challenges that organizations are constantly overcoming:
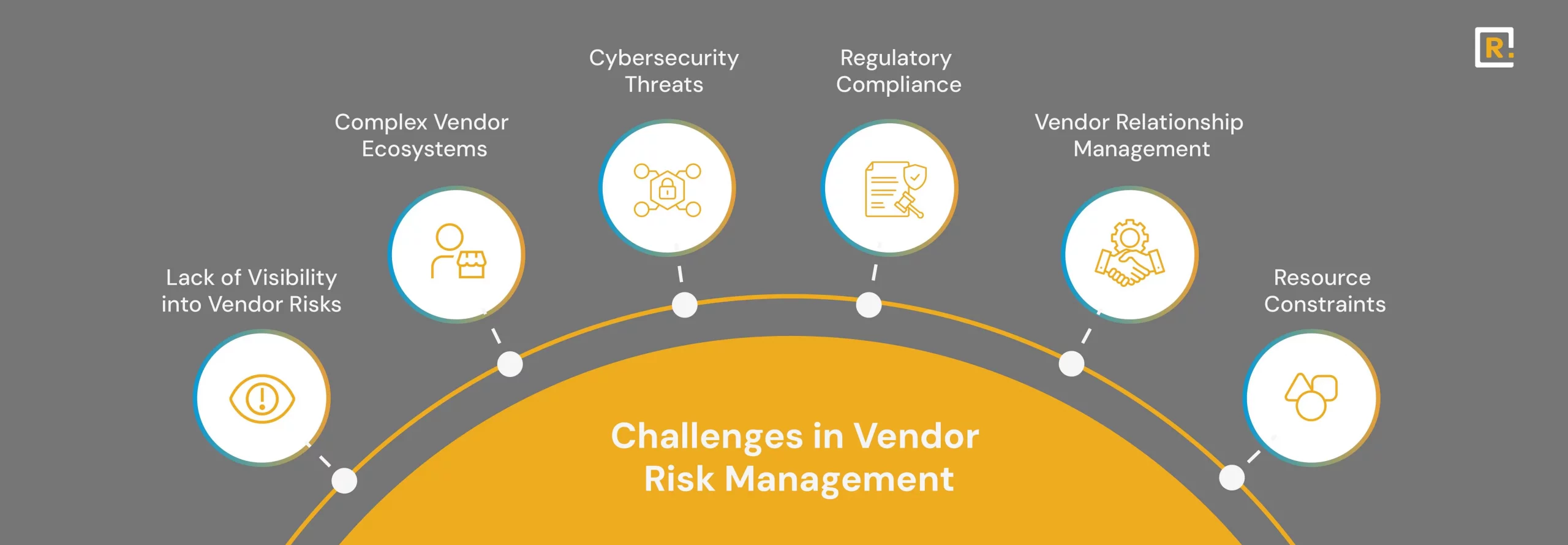
Lack of Visibility into Vendor Risks
One of the enormous challenges in VRM is gaining visibility into the risks vendors pose. Collecting and analyzing data about a vendor’s operations, finances, current security measures, and compliance status takes time. Non-transparency often results in an inability to get a feel for the actual level of risk a vendor may present.
Complex Vendor Ecosystems
Large organizations often rely on hundreds or thousands of vendors, each with a characteristic risk profile. That makes vendor management extensive and complex, including risk assessment and continuous monitoring of many vendors. Management of such enormous complexity without automated tools can lead to mistakes, missed risks, and inefficiencies.
Cybersecurity Threats
As the sophistication of the threats increases, the possibility of cyber threats coming from a vendor also grows. Indeed, most organizations need help to ensure their vendors are cyber-secure or can adhere to strict security standards. For this reason, cybersecurity risk is one of the most challenging aspects of VRM to control effectively.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a moving target as laws and industry standards change. Continuing to support harmony with changing laws and industry standards and making all vendors conform to the most recent sets of regulations presents difficulty. This aspect of corporate life is complicated for businesses operating in many regions or industries that have imposed strict compliance rules.
Vendor Relationship Management
It’s often the fine line between maintaining good vendor relationships and eliminating risks. Too heavy-handed risk management agreements can stress vendor relationships, while inadequate supervision means they are taking more risks. Organizations must walk the fine line in managing vendor risks while creating a solid and positive relationship.
Resource Constraints
Many companies must be more resource-constrained regarding personnel, budget, or technology to oversee vendor risk. Conducting thorough due diligence, continuous monitoring, and enforcing compliance requirements takes time and effort. These constraints occasionally arise in smaller organizations or from tight budgets for risk management initiatives.
How to Implement Vendor Risk Management?
An effective vendor risk management program needs to be systematically implemented. If the following steps are followed, firms will be better placed to develop a VRM framework that considers vendors’ risks to business operations.
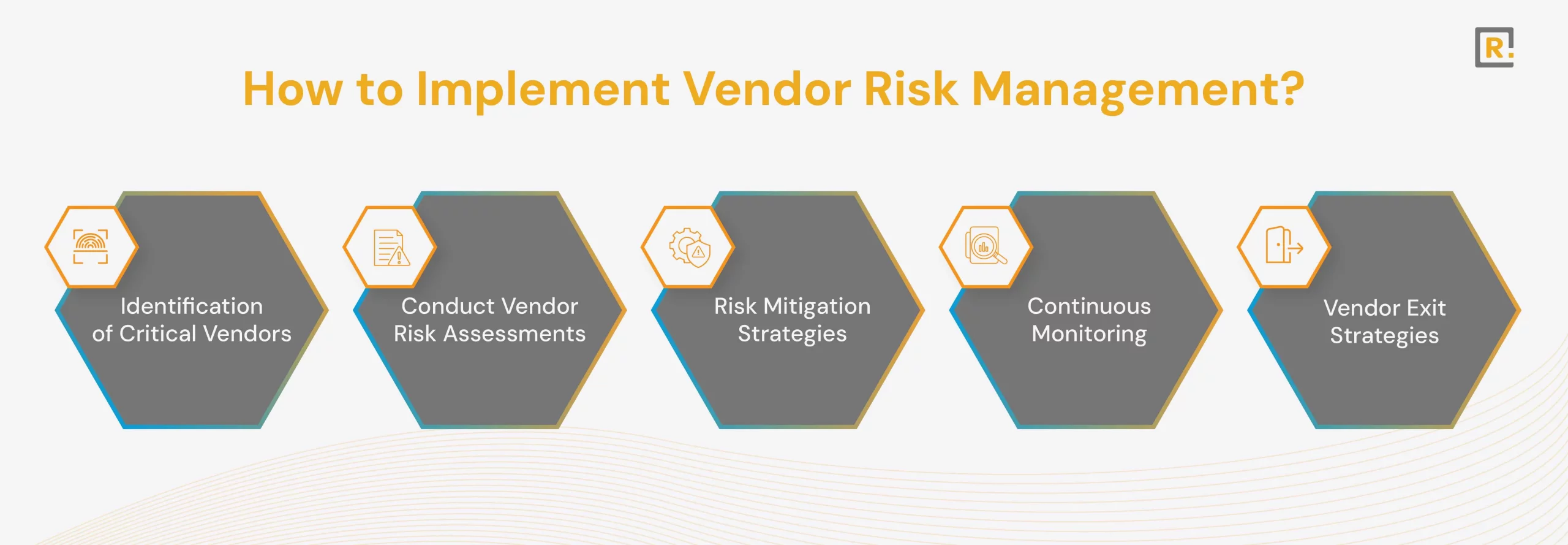
Identification of Critical Vendors
The very first step of the VRM program is the identification of critical vendors regarding the business operations.
When they fail, these vendors can disrupt operations, cause financial losses, and expose the organization to compliance risk. After identifying the vendor, you may prioritize it for further risk assessments and monitoring.
Conduct Vendor Risk Assessments
After identifying the critical vendors, the next step is to conduct a detailed risk assessment of each one. That would mean assessing the financial stability, level of cybersecurity, adherence to compliance, performance history, etc.
It is about identifying the risks that might fall out before they happen and the mitigation strategies against them.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
The risk mitigation strategies follow the identification of the risks. These strategies may include additional security measures, contract revision with more stringent SLAs, and portfolio diversification to decrease dependence on any one vendor. The risk mitigation strategy should be aligned with the specific risks that each vendor poses.
Continuous Monitoring
These vendor risks are not static. They will change over time based on the vendor’s financial situation, shifting regulatory requirements, and the appearance of new cybersecurity threats.
In this respect, continual monitoring is critical to identifying and mitigating new risks as they emerge. This includes periodic vendor performance reviews, audits, and updates on vendor financial health or compliance status changes.
Vendor Exit Strategies
A clear vendor exit strategy will become critical for mitigating the risks related to terminating relationships with vendors, whether due to bad performance or legal issues, or an exit strategy to ensure a smooth transition out of a vendor, ensuring minimum disruption to your business. This would prevent data from being released or destroyed.
How Does Raapyd Provide Vendor Risk Management Solutions to Businesses?
Raapyd is a global vendor risk management solution supplier that helps companies identify, assess, and mitigate the overall risk coming from third-party vendors. Its solution unites cutting-edge technology and industry experience, offering businesses the tools to protect operations from vendor-related risk.
End-to-End Vendor Risk Assessment Tools
Raapyd provides the organization with strong risk assessment tools to assess vendors’ risks in real-time. It provides detailed insight into a vendor’s financial stability, cybersecurity practices, and compliance status, helping businesses make informed decisions while partnering with any vendor.
Automated Vendor Monitoring
Raapyd’s vendor monitoring solutions automate the tracking of vendor performance, security incidents, and compliance status. It supports the organization in detecting emerging risks early enough to take proactive measures against their manifestation.
Risk scoring models: Customizable
Raapyd can enable vendor prioritization for more critical organizations by offering customizable risk-scoring modeling. By assigning risk scoring to every vendor, organizations could prioritize their risk management efforts toward the most important vendors and ensure the execution of relevant mitigation strategies.
Regulatory Compliance Support
Raapyd’s solutions are designed to help businesses adhere to industry-specific regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. The platform automates compliance tracking and reporting, taking the burden off of organizations to ensure vendors meet all necessary regulatory requirements.
Vendor Performance Analytics
Raapyd’s platform provides detailed analytics into vendor performance, enabling businesses to track their key metrics regarding SLA compliance, delivery times, and quality of service. These analytics provide great insight into the reliability of the vendors and help fine-tune the relationship between them and the organization.
Conclusion
Vendor Risk Management is an intrinsic part of contemporary business practices. As organizations increasingly depend on third-party vendors for core services, their risks with vendor relationships grow accordingly. With a well-developed VRM program, an organization can be shielded from operational threats, better safeguarded about sensitive data, and more likely to meet regulatory requirements.
A business’s best practices for managing vendor risks are due diligence, vendor risk rating or categorization, robust contracts, and ongoing performance monitoring. Although some challenges may be associated with VRM, the benefits of protecting your organization from vendor-related threats far outweigh the cost.
Partnering with an experienced vendor risk management solution provider like Raapyd can make things easier by arming businesses with the tools and insights they need to manage vendor-related risks effectively. An attitude toward proactive VRM equips organizations with the means to ensure business, reputation, and bottom-line protection in today’s ever-connected world.
Discover More
Enhance Your Vendor Procurement Process
Empower your business with effective vendor risk management strategies.
